Sunday, November 16, 2014
Tuesday, November 11, 2014
Upcoming Webinar Event - Groundwater Levels, Extraction and Climate Connections in the United States, 1949-2009.
The next Penn State Water Resources Extension webinar on Wednesday, November 19, 2014 from 12:00 to 1:00 PM EST will discuss Groundwater Levels, Extraction and Climate Connections in the United States, 1949-2009. The presenter will be Dr. Tess Russo, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Geosciences at Penn State University.
When: Wednesday, November 19, 2014 - 12:00 to 1:00 PM
Title: Groundwater Levels, Extraction and Climate Connections in the United States, 1949-2009Presenter: Tess Russo, Assistant Professor, Department of Geosciences, Penn State University
Where: the live webinar can be viewed at https://meeting.psu.edu/water1
Webinar description:
Groundwater constitutes a critical component of our water resources, especially during dry seasons and droughts, and in regions lacking reliable access to surface water. This seminar will cover the results of a continental-scale study revealing groundwater depletion trends. Analysis of historical groundwater level records indicates groundwater storage declined between 1949 and 2009 throughout much of the continental United States. Most notably, groundwater level declines in the southern and eastern U.S. are comparable to declines in areas of the often-discussed water stressed areas of the High Plains and southwest U.S. The causes of groundwater level change are multifaceted, varying in time and space across the U.S. Correlations between pumping rate and groundwater level were observed in a majority of counties. Climate is also clear controlling factor on groundwater levels, with changes in groundwater level correlating well with long-term climate patterns including the Pacific Decadal Oscillation.
About the Presenter:
Tess Russo is a hydrologist who focuses on quantifying hydrologic system responses to environmental change with the objective of informing management and restoration decisions. Tess received her Ph.D. from the University of California, Santa Cruz, and was an Earth Institute Postdoctoral Fellow at Columbia University before joining the Geosciences Department at Penn State as an assistant professor in August 2014. Her research interests include riparian flow and solute dynamics, managed aquifer recharge, and agricultural water management, including quantification of both regional-scale water availability and field-scale transport of agrochemicals. Tess currently has projects in India, Kenya, Tanzania, Papua New Guinea, and the United States.
How to Participate
Additional webinars on various water resources topics will be offered each month - generally on the last Wednesday of the month. A full schedule of upcoming webinars can be found at: http://extension.psu.edu/
Bryan Swistock
Water Resources Extension Specialist
Penn State University
When: Wednesday, November 19, 2014 - 12:00 to 1:00 PM
Title: Groundwater Levels, Extraction and Climate Connections in the United States, 1949-2009Presenter: Tess Russo, Assistant Professor, Department of Geosciences, Penn State University
Where: the live webinar can be viewed at https://meeting.psu.edu/water1
Webinar description:
Groundwater constitutes a critical component of our water resources, especially during dry seasons and droughts, and in regions lacking reliable access to surface water. This seminar will cover the results of a continental-scale study revealing groundwater depletion trends. Analysis of historical groundwater level records indicates groundwater storage declined between 1949 and 2009 throughout much of the continental United States. Most notably, groundwater level declines in the southern and eastern U.S. are comparable to declines in areas of the often-discussed water stressed areas of the High Plains and southwest U.S. The causes of groundwater level change are multifaceted, varying in time and space across the U.S. Correlations between pumping rate and groundwater level were observed in a majority of counties. Climate is also clear controlling factor on groundwater levels, with changes in groundwater level correlating well with long-term climate patterns including the Pacific Decadal Oscillation.
About the Presenter:
Tess Russo is a hydrologist who focuses on quantifying hydrologic system responses to environmental change with the objective of informing management and restoration decisions. Tess received her Ph.D. from the University of California, Santa Cruz, and was an Earth Institute Postdoctoral Fellow at Columbia University before joining the Geosciences Department at Penn State as an assistant professor in August 2014. Her research interests include riparian flow and solute dynamics, managed aquifer recharge, and agricultural water management, including quantification of both regional-scale water availability and field-scale transport of agrochemicals. Tess currently has projects in India, Kenya, Tanzania, Papua New Guinea, and the United States.
How to Participate
- The live webinar will occur from 12:00 to 1:00 PM and is accessible at: https://meeting.psu.edu/water1
- You can access this webinar simply by signing in as a "guest".
- Taped versions of each webinar in the series are available at: http://extension.psu.edu/
water/webinar-series/past- webinars - If you have not registered for past water webinars, please visit the following website to register so we can keep you updated about future webinar offerings: http://extension.psu.edu/
water/webinar-series/schedule/ registration - If this will be your first webinar, you may want to test your computer and internet connection for compatibility at:https://meeting.psu.edu/
common/help/en/support/ meeting_test.htm
Additional webinars on various water resources topics will be offered each month - generally on the last Wednesday of the month. A full schedule of upcoming webinars can be found at: http://extension.psu.edu/
- December 17, 2014 – The Development of Sustainable Bioremediation Technologies to Solve Global Water Challenges, Dr. Rachel Brennan, Penn State University
Bryan Swistock
Water Resources Extension Specialist
Penn State University
Water and Hydrogeology of Watersheds
The following blog post is a summary of material found in Chapter 3, Water and Hydrogeology of Watersheds from the text by Kaufman, M., Rogers, D., and Murry, Kent. 2011. Urban Watersheds; Geology, Contamination, and Sustainable Development. Taylor and Francis Group, LLC. Boca Raton, FL.
Clean water is essential to maintain health of all species
on earth. Water and geology help to shape our natural environment. We are
learning more and more about how human impacts in the natural and built
environmental are impacting our ground and surface waters.
Groundwater in
Watersheds
Groundwater is defined as “any water beneath the surface of
the ground”. Apart from the bound water in icecaps and glaciers, over 95% of
all freshwater sources on Earth come from groundwater. Imagine poring all the
earth’s groundwater out onto the US land surfaces, it would spread to a depth of
a half-mile. On a global scale, if water covered all land surfaces, the water
would be 150’ deep. The total amount of groundwater on Earth is 100 times more
than all the visible surface water in lakes, streams, rivers, and swamps.
Much of the groundwater of the US is found in aquifers. An
aquifer is considered a “mappable geologic
unit” that is created by water-saturated porous media, usually sands and gravels,
which have the capacity to store and move large amounts water. Finer grained
materials like clay and silt may not transmit water quickly enough to be
considered as an aquifer media. Up to 50% of the US population obtains its
drinking water from groundwater sources. In addition, agriculture uses groundwater at about 40% for irrigation of crops.
Groundwater is in constant motion under the force of gravity
and moves from higher to lower areas of pressure. Movement occurs through a system
of passageways of unsaturated pore spaces in soils and sediment. This zone of
aeration is known as the vadose
zone.
Pressure is naturally higher under mountains and hills due to mass and valleys are under lower pressure; resulting in a pressure gradient where groundwater flows to the surface and can interact with surface water.
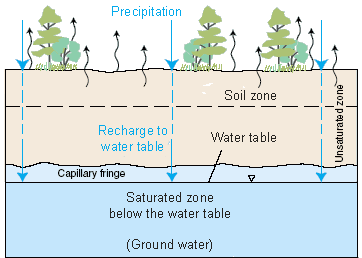 |
| Sourced: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/graphics/wcinfiltrationsoilzone.gif |
Pressure is naturally higher under mountains and hills due to mass and valleys are under lower pressure; resulting in a pressure gradient where groundwater flows to the surface and can interact with surface water.
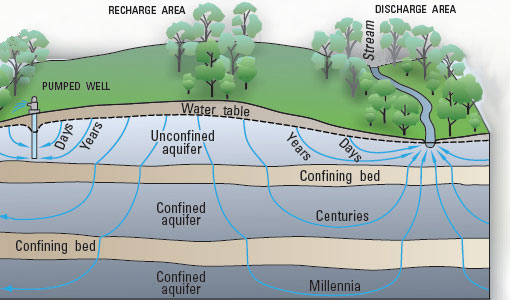 |
| Sourced: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/graphics/wcgwdischarge.jpg |
Groundwater and
Surface Waters
 |
| Sourced: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/watercyclesummary.html |
Groundwater and surface waters are interconnected in watersheds. Climate, vegetation, topography, rainfall, and geology all influence patterns of surface water flow and drainage density.
Ground water provides an important influx of water to
surface waters that serves to protect aquatic life through periods of low
precipitation and drought. Streams, lakes and wetlands can gain groundwater;
conversely surface waters can flow into groundwater. Soils with low
conductivity in the vadose zone can impair ground and surface water
communication. Additionally, a lowering of the water table due to drought,
local geology, or excessive groundwater use can impair connectivity.
Important research must be done on ground and surface water
connectivity within urban areas. Toxins and pollutants, like those found in the
first flush of stormwater runoff can contaminate groundwater that is close to
the surface. Groundwater contamination also has the ability to reach surface
waters. Additionally, removal of large groundwater quantities near a surface
water body can cause some loss of the surface waters; impairing aquatic
functions.
Urban area watershed influences are numerous and can
include: runoff from impervious surfaces creates increased erosion and
sedimentation, petroleum-based contaminants from vehicles, groundwater
contamination from industry, wetland destruction, wastewater discharge,
combined sewer overflows (CSOs), aging infrastructure, stream bed alterations,
other point and non-point pollution sources, dam construction altering
groundwater levels, and natural drainage system alterations.
Building Climate Resilience in Communities
The Watershed Academy is a program developed by the EPA's Office of Water. The goal is to provide information and training for professionals seeking to learn and implement watershed approaches to natural resource conservation and urban management.
Through this free program, individuals can complete self-directed training lessons and earn a certificate of professional development. Available training also includes monthly live web-based seminars on relevant topics. I participated in a live webcast on Climate Resilience; What to Expect, How to Prepare, and What You Can Learn From Others. Previous webcasts are also available online.
Resiliency is the concept of communities being about to dynamically adapt in the face of a changing climate. The webcast included information from the National Climate Assessment Report, the new Workbook for Developing Risk-Based Adaption Plans, and a case-study of the San Juan National Estuary Program that implemented the adaption plan using the risk-based principles.
In response to the President's Better Buildings Challenge, the City of Roanoke has made the commitment to reduce energy consumption by 20 % in public buildings by 2020. As of May 2014, headway has been made with Roanoke achieving 11% improvement in building energy performance. Read the full White House Press Release Fact Sheet on What Climate Change Means for Virginia here.
Thursday, November 6, 2014
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
